 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站! 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
截止目前,引用Bioss產品發表的文獻共28124篇,總影響因子134574.75分,發表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等頂級期刊的文獻共66篇,合作單位覆蓋了清華、北大、復旦、華盛頓大學、麻省理工學院、東京大學以及紐約大學等國際研究機構上百所。
我們每月收集引用Bioss產品發表的文獻。若您在當月已發表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,請致電Bioss,我們將贈予現金鼓勵,金額標準請參考“發文章 領獎金"活動頁面。
近期收錄2023年12月引用Bioss產品發表的文獻共307篇(圖一,綠色柱),文章影響因子(IF) 總和高達2153.1,其中,10分以上文獻44篇(圖二)。
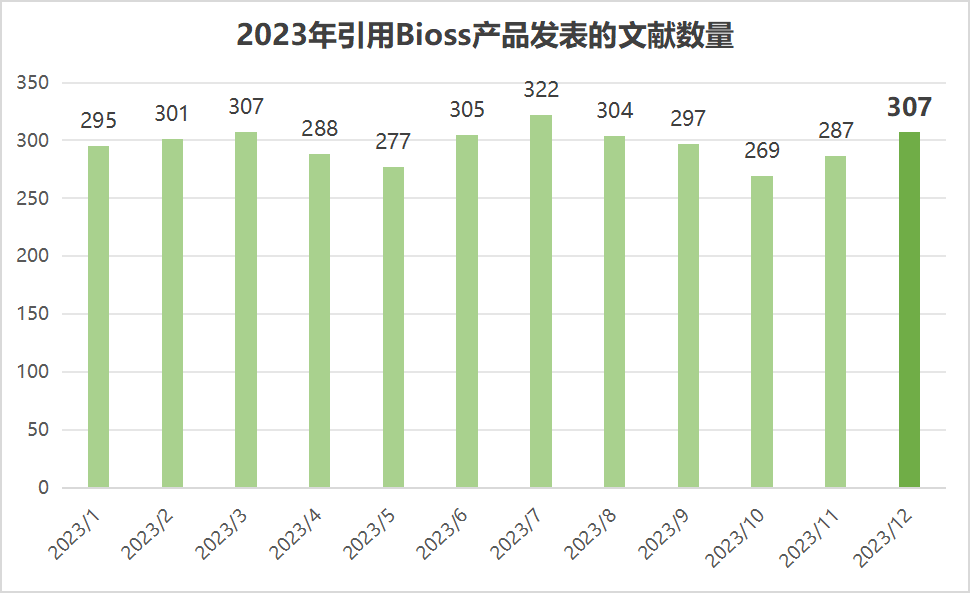
圖一
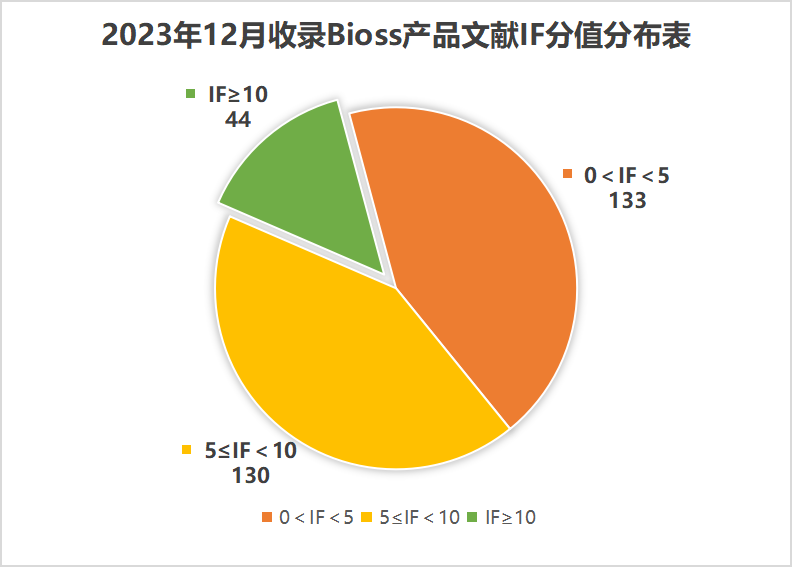
圖二
本文主要分享引用Bioss產品發表文章至Nature, Cell, Immunity, Cancer Cell等期刊的5篇 IF>15 的文獻摘要,讓我們一起欣賞吧。
Nature [IF=64.8]

文獻引用抗體:bs-41176P
Recombinant human Beta-2-microglobulin | FC
作者單位:中山大學
摘要:Emerging data have shown that previously defined noncoding genomes might encode peptides that bind human leukocyte antigen (HLA) as cryptic antigens to stimulate adaptive immunity. However, the significance and mechanisms of action of cryptic antigens in anti-tumour immunity remain unclear. Here mass spectrometry of the HLA class?I (HLA-I) peptidome coupled with ribosome sequencing of human breast cancer samples identified HLA-I-binding cryptic antigenic peptides that were noncanonically translated by a tumour-specific circular RNA (circRNA): circFAM53B. The cryptic peptides efficiently primed naive CD4+ and CD8+ T?cells in an antigen-specific manner and induced anti-tumour immunity. Clinically, the expression of circFAM53B and its encoded peptides was associated with substantial infiltration of antigen-specific CD8+ T?cells and better survival in patients with breast cancer and patients with melanoma. Mechanistically, circFAM53B-encoded peptides had strong binding affinity to both HLA-I and HLA-II molecules. In vivo, administration of vaccines consisting of tumour-specific circRNA or its encoded peptides in mice bearing breast cancer tumours or melanoma induced enhanced infiltration of tumour-antigen-specific cytotoxic T?cells, which led to effective tumour control. Overall, our findings reveal that noncanonical translation of circRNAs can drive efficient anti-tumour immunity, which suggests that vaccination exploiting tumour-specific circRNAs may serve as an immunotherapeutic strategy against malignant tumours.
Cell [IF=64.5]

文獻引用抗體:bs-5977R
c-Maf Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:中國科學院動物研究所
摘要:Different functional regions of brain are fundamental for basic neurophysiological activities. However, the regional specification remains largely unexplored during human brain development. Here, by combining spatial transcriptomics (scStereo-seq) and scRNA-seq, we built a spatiotemporal developmental atlas of multiple human brain regions from 6-23 gestational weeks (GWs). We discovered that, around GW8, radial glia (RG) cells have displayed regional heterogeneity and specific spatial distribution. Interestingly, we found that the regional heterogeneity of RG subtypes contributed to the subsequent neuronal specification. Specifically, two diencephalon-specific subtypes gave rise to glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons, whereas subtypes in ventral midbrain were associated with the dopaminergic neurons. Similar GABAergic neuronal subtypes were shared between neocortex and diencephalon. Additionally, we revealed that cell-cell interactions between oligodendrocyte precursor cells and GABAergic neurons influenced and promoted neuronal development coupled with regional specification. Altogether, this study provides comprehensive insights into the regional specification in the developing human brain.
Nature Nanotechnology[IF=38.3]

文獻引用產品:bs-0295G-AF488
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L / AF488 | ICC
作者單位:中國科學院高能物理研究所
摘要:Trained immunity enhances the responsiveness of immune cells to subsequent infections or vaccinations. Here we demonstrate that pre-vaccination with bacteria-derived outer-membrane vesicles, which contain large amounts of pathogen-associated molecular patterns, can be used to potentiate, and enhance, tumour vaccination by trained immunity. Intraperitoneal administration of these outer-membrane vesicles to mice activates inflammasome signalling pathways and induces interleukin-1β secretion. The elevated interleukin-1β increases the generation of antigen-presenting cell progenitors. This results in increased immune response when tumour antigens are delivered, and increases tumour-antigen-specific T-cell activation. This trained immunity increased protection from tumour challenge in two distinct cancer models.
Military Medical Research [IF=21.1]

文獻引用產品:bs-1427R
IRAK2 Rabbit pAb | IGS
作者單位:空軍軍醫大學西京醫院
摘要:The expression of Adipsin was significantly downregulated in the HFD-induced DCM model (P?<?0.05). Adipose tissue-specific overexpression of Adipsin significantly improved cardiac function and alleviated cardiac remodeling in DCM (P?<?0.05). Adipsin overexpression also alleviated mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation function in diabetic stress (P?<?0.05). LC–MS/MS analysis, GST pull-down technique and Co-IP studies revealed that interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-like 2 (Irak2) was a downstream regulator of Adipsin. Immunofluorescence analysis also revealed that Adipsin was co-localized with Irak2 in cardiomyocytes. Immunocolloidal gold electron microscopy and Western blotting analysis indicated that Adipsin inhibited the mitochondrial translocation of Irak2 in DCM, thus dampening the interaction between Irak2 and prohibitin (Phb)-optic atrophy protein 1 (Opa1) on mitochondria and improving the structural integrity and function of mitochondria (P?<?0.05). Interestingly, in the presence of Irak2 knockdown, Adipsin overexpression did not further alleviate myocardial mitochondrial destruction and cardiac dysfunction, suggesting a downstream role of Irak2 in Adipsin-induced responses (P?<?0.05). Consistent with these findings, overexpression of Adipsin after Irak2 knockdown did not further reduce the accumulation of lipids and their metabolites in the cardiac myocardium, nor did it enhance the oxidation capacity of cardiomyocytes expose to palmitate (PA) (P?<?0.05). These results indicated that Irak2 may be a downstream regulator of Adipsin.
Bioactive Materials[IF=18.9]

文獻引用抗體:bs-1559R
GLP-1R Rabbit pAb | WB
作者單位:北京大學人民醫院圖片
摘要:Nonunions and delayed unions pose significant challenges in orthopedic treatment, with current therapies often proving inadequate. Bone tissue engineering (BTE), particularly through endochondral ossification (ECO), emerges as a promising strategy for addressing critical bone defects. This study introduces mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing Exendin-4 (MSC-E4), designed to modulate bone remodeling via their autocrine and paracrine functions. We established a type I collagen (Col-I) sponge-based in vitro model that effectively recapitulates the ECO pathway. MSC-E4 demonstrated superior chondrogenic and hypertrophic differentiation and enhanced the ECO cell fate in single-cell sequencing analysis. Furthermore, MSC-E4 encapsulated in microscaffold, effectively facilitated bone regeneration in a rat calvarial defect model, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic agent for bone regeneration. Our findings advocate for MSC-E4 within a BTE framework as a novel and potent approach for treating significant bone defects, leveraging the intrinsic ECO process.